Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has no objective diagnosis method despite having a high prevalence. Machine learning has been widely used to develop classification models for ASD using neuroimaging data. Recently, studies have shifted towards using large multi-site neuroimaging datasets to boost the clinical applicability and statistical power of results. However, the classification performance is hindered by the heterogeneous nature of agglomerative datasets.
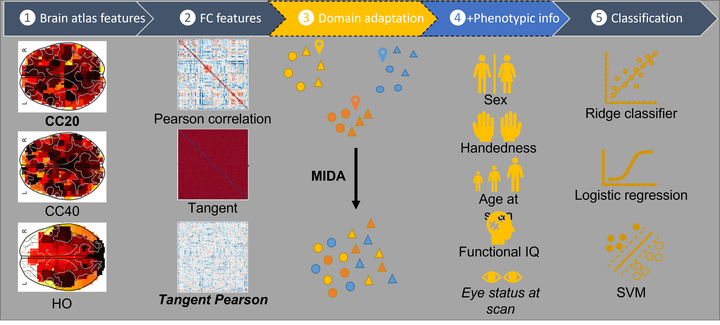
In this project, we propose new methods for multi-site autism classification using the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) dataset. We firstly propose a new second-order measure of functional connectivity (FC) named as Tangent Pearson embedding to extract better features for classification. Then we assess the statistical dependence between acquisition sites and FC features, and apply a domain adaptation approach to minimise the site dependence of FC features to improve classification. Our analysis shows that 1) statistical dependence between site and FC features is statistically significant at the 5% level, and 2) extracting second-order features from neuroimaging data and minimising their site dependence can improve over state-of-the-art classification results on the ABIDE dataset, achieving a classification accuracy of 73%.