Neighborhood aggregation is a key step in Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) for graph representation learning. Two commonly used aggregators, sum and mean, are designed with the homophily assumption that connected nodes are likely to share the same label. However, real-world graphs are noisy and adjacent nodes do not necessarily imply similarity.Learnable aggregators are proposed in Graph Attention Network (GAT) and Learnable Graph Convolutional Layer (LGCL). However, GAT considers node importance but not the importance of different features. The convolution aggregator in LGCL considers feature importance but it can not directly operate on graphs due to the irregular connectivity and lack of orderliness.
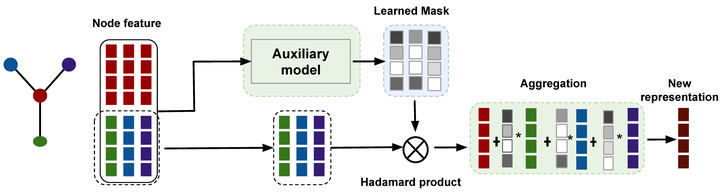
In this work, we firstly unify the current learnable aggregators in a framework: Learnable Aggregator for GCN (LA-GCN) by introducing a shared auxiliary model that provides a customized schema in neighborhood aggregation. Under this framework, we propose a new model called LA-GCNMask consisting of a new aggregator function,mask aggregator. The auxiliary model learns a specific mask for each neighbor of a given node, allowing both node-level and feature-level attention. This mechanism learns to assign different importance to both nodes and features for prediction, which provides interpretable explanations for prediction and increases the model robustness. Experiments on seven graphs for node classification and graph classification tasks show that LA-GCNMask outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, our aggregator can identify both the important nodes and node features simultaneously, which provides a quantified understanding of the relationship between input nodes and the prediction. We further conduct experiments on noisy graphs to evaluate the robustness of our model. Experiments show that LA-GCNMask consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, with up to 15% improvements in terms of accuracy compared to the second best.